
A geometric distribution is a distribution in which there is a series of repeated and independent trials (Bernoulli trials with a chance of success or failure), with a fixed chance of success (P).
Unlike the binomial distribution, which also consists of a series of Bernoulli trials, the geometric distribution has one success and it only occurs at the end. When success comes – the series of experiments ends.
Geometric distribution is infinite, meaning there is a chance of success the first time, the second time, the third time, the tenth time, the hundredth time, etc.
Mathematically we will define the distribution with a chance of success P, therefore with a chance of failure is 1-P.
The chance of success the K time is:
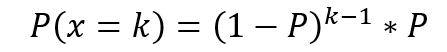
Expected value of number of trials until a success arrives:
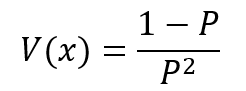
Question for example:
On his day off, John free throws with a chance of success of 0.82.
- What is the probability that he will succeed the 4th time?
- What is the chance that he will succeed at least the 3rd time?
- What is his expectation of success?
- What are the variance and standard deviation of his success?
Answer:
Part 1:
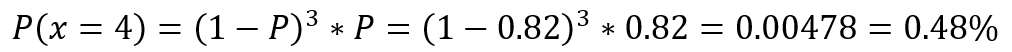
Part 2:

Part 3:

Part 4:

